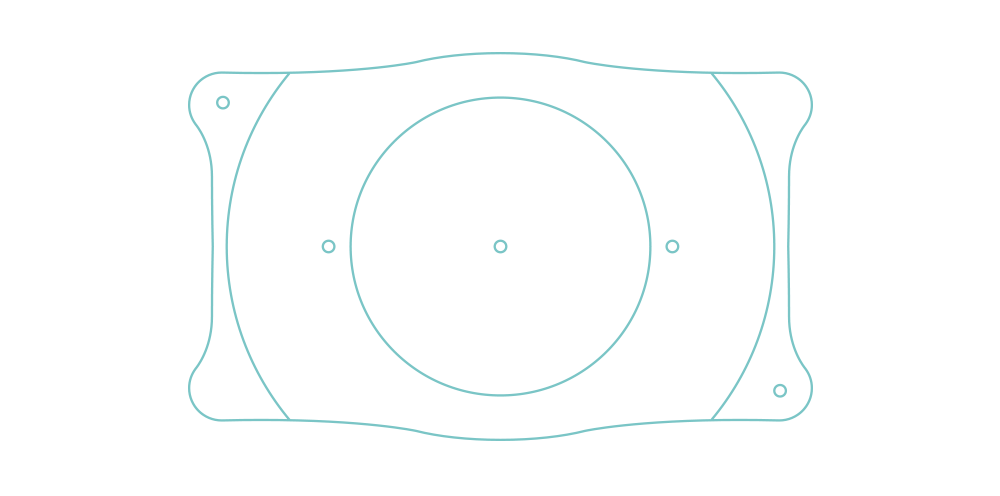
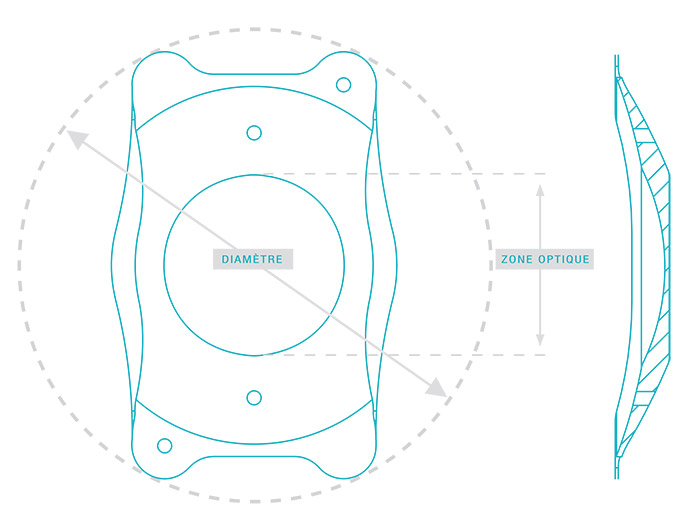
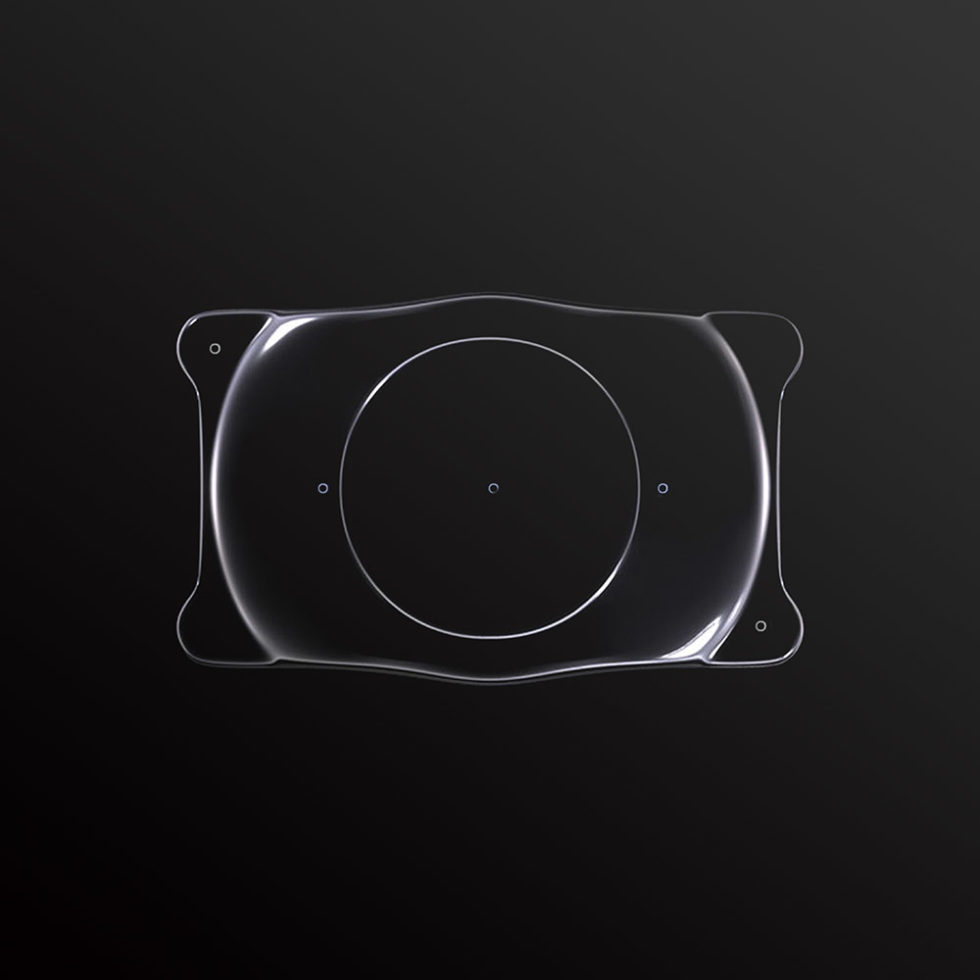
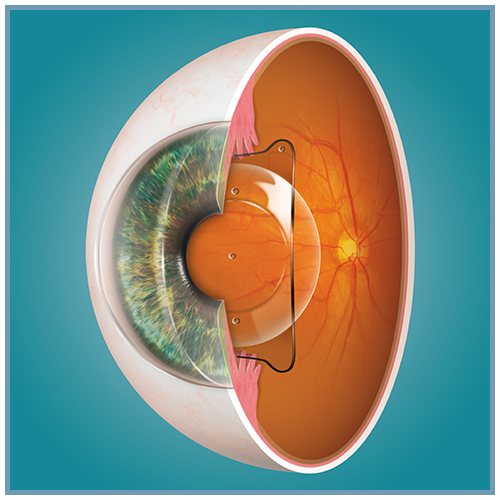
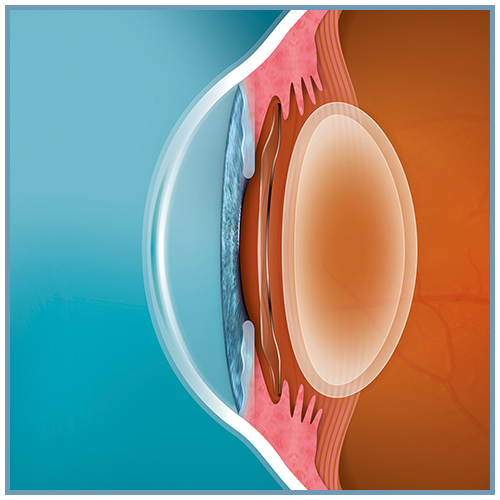
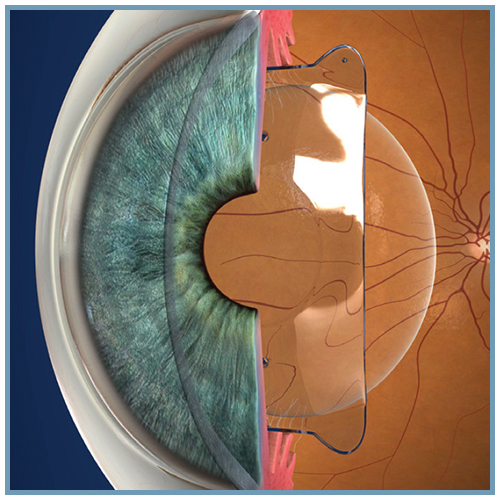
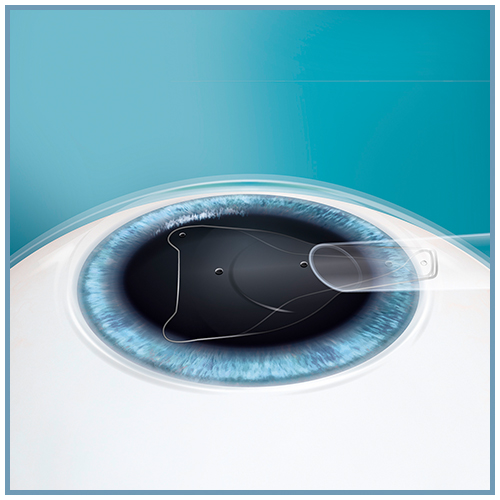
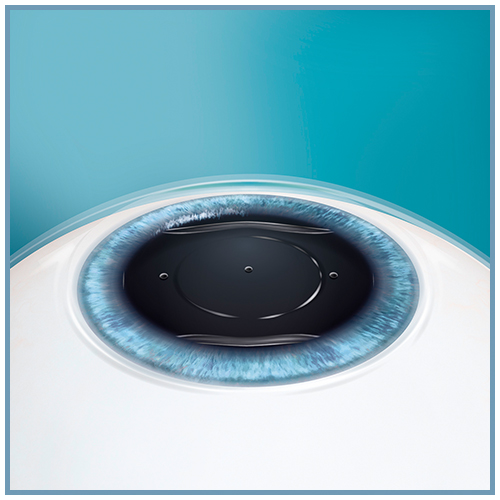
Les lentilles sphériques et toriques EVO ICL™ (sphériques : EVO ICL™, EVO+ ICL™, Visian® ICL™ / toriques : Evo Toric ICL™, EVO+ Toric ICL™, Visian® Toric ICL™) sont des lentilles intraoculaires phaques pour implantation en chambre postérieure.
Dispositif médical de classe III / CE 0344 / Non soumis au remboursement par les organismes d’assurance maladie.
Fabricant : STAAR Surgical AG
Importateur : Ophta-France
Organisme notifié : DEKRA
Ces informations techniques sont à destination des professionnels de santé. Pour un bon usage du produit, merci de vous reporter à la notice du produit.